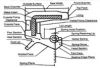
Technical data
NBR characteristics (nitril butadien rubber):
Acrylonitrile rubber is a copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene. The quantitative relation of these compounds determines the properties of vulcanizates, and especially their oil resistance or freeze resistance. The acrylonitrile content in the rubber can amount from 18% to 50%. Together with the growth of the acrylonitrile quantity there is an increase in resistance to oil and aliphatic solvents as well as resistance to higher temperatures while simultaneous reducing resistance to low temperatures.
The acrylonitrile rubber vulcanizates are characterized with high elasticity, breaking strength, a slight permanent deformation while being pressed and with resistance to oils. Most seals used in hydraulics and pneumatics are manufactured on the basis of nitryl rubber. The temperature range of acrylonitrile rubber application amounts: from -30 to +100 C (water), short-duration to 120 C.
Nitril vulcanizates are resistant to: aliphatic hydrocarbons, propane, butane, benzine, petroleum, mineral oils and greasing substances, vegetable and animal oils, motor oils, transformer oil, fuel? oils, light fuel oils and fuels for diesel engines, nonflammable hydraulic liquids such as HSA, I-HSB (oil and water emulsions and water and oil emulsions) and HSC (mixtures of poly-glycol and water), dilute acids and lukewarm bases. Nitril vulcanizates are not resistant to: aromatic hydrocarbons (arenes), and chlorinated hydrocarbons (e.g. benzene, trichloroethylene, tetrachloromethane - tetra), esters, polar solvents, silicone oils and greasing substances, slow-burning hydraulic liquids such as HSD (based on polyester plastics and chlorinated hydrocarbons), brake fluids on the basis of glycols (blue).
| Konstrukcja uszczelnienia Simmering GRN | Odmiana uszczelnienia | Kauczuk bazowy, twardość | Temperaturowy zakres pracy w powietrzu oC | Środowiska robocze |
 | Z wargą pyłochronną | Nitrylowy, NBR 70 | od -30oC do + 100OC | -oleje, smary mineralne-oleje pochodzenia roślinnego zwierzęcego-węglowodory alifatyczne-woda do + 100oC-rozcięczone roztwory kwasów i zasad do +50 oC-niepalne ciecze hydrauliczne typu HSA i HSB |
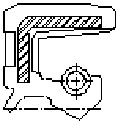
| Konstrukcja uszczelnienia pierścienia O-ring GRN | Odmiana uszczelnienia | Kauczuk bazowy, twardość | Temperaturowy zakres pracy w oC | Środowiska robocze |
 | Przekrój kołowy | Nitrylowy, NBR 70 | od -30oCdo + 100oC | -oleje, smary mineralne-oleje pochodzenia roślinnego zwierzęcego-węglowodory alifatyczne-woda do + 100oC-rozcięczone roztwory kwasów i zasad do +50 oC-niepalne ciecze hydrauliczne typu HSA i HSB |
Use:
for movable and static connections in hydraulic and pneumatic devices and in other connections of various parts of machines and devices.
General information about bearings
In order to ensure proper operation of moving machine parts rotary motion (axes, shafts and machine parts embedded on them) should be kept fixed position relative to the axis of rotation of shafts fixed base (eg body machine).
Fulfill this task bearings and positioning axes and shaft relative to the body of machinery called a bearing.
Bearings are subject to the forces resulting from the weight of the shaft and mounted on their components (gears, pulleys, couplings, etc.) and the forces coming from the load and axle shafts. Have a bearing on the shaft reaction equal in value to the load-bearing forces and returned to the contrary (like the reactions of the supports in beams).
To meet the given task bearings, that provide rotary motion of the shaft, and maintain a constant position of the axis of rotation, and carried the load, should be characterized by small resistance movement, a stable job, reliability and resistance to wear, which is very durable. They should also meet specific requirements of technology and design.
Bearings divided into sliding and rolling.
The slide bearing surface of the pivot shaft slides along the surface of the acetabulum (the bearing cooperating with a pin), or directly on the surface of the bearing hole, so that during operation there is a sliding friction.
The roller bearings between the mating surfaces of the journal and the bearing rolling elements are located (eg balls) and then instead of sliding friction is rolling friction. The following are examples of the two types of bearings also indirectly determine their advantages and disadvantages.
Plain bearings are generally used:
- The transfer of very heavy loads (up to several MN-in
- For bearings with a diameter of 1 m), and the shock loads when it is necessary to suppress vibrations of the bearing shaft,
- At high speeds and the possibility of obtaining fluid friction,
- If necessary, the use of bearings (or pan) shared when low noise is required for the bearing,
- The achievement of high accuracy assembly (required for rolling bearings) is difficult,
- In small structures with very small loads (eg. In precision engineering equipment).
Bearings are the most common:
- If we want to obtain a very small resistance at work, especially at start-up,
- At varying shaft speeds (because the coefficient of friction bearings in a very small extent depends on speed)
- The frequent stopping and starting of machines (such as working conditions bearings wear out too quickly)
- The required high reliability and long life bearings,
- Where, due to the dimensions of the body of the machine it is necessary to use bearings with a small longitudinal dimensions.
Select the type of bearings (sliding or rolling) may also depend on several other factors: the operating conditions, the construction of the shaft, the mode of lubrication (dependent, among others. Bring the capabilities of grease into the bearing), the technical reasons related to the repair and replacement of bearings etc.
Classification and characteristics of bearings.
Depending on the direction of load acting on the bearing, there are bearings:
- Transverse, intended for receiving loads perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
- Longitudinal, loaded with forces acting in the direction of the axis of rotation.
- Angular designed to accommodate load both perpendicular to and in line with the direction of the axis of rotation.
In order to reduce the resistance of sliding movement between the surfaces of the bushing and the pin must be formed a layer of grease or carrier gas (usually air).
Depending on the mode of administration is distinguished bearing grease:
- Hydrostatic (aerostatyczne) in which the carrier layer of lubricant (gas) is fed under pressure,
- Hydrodynamic (aerodynamic), in which the carrier layer of lubricant (gas) is created by the rotation of the pivot bushing and the reciprocal sliding between the sliding surfaces.
Lubrication of air bearings are used in devices with limited capacity, but with very high speeds - from 40 000 to 360 000 rev / min, such as microturbines grinding spindles, dental and surgical drills.
Friction in plain bearings.
Sliding friction occurring between the bearing and the bushing with shaft depends on the materials of the working elements, the condition (roughness) of the surface, and the type of lubrication of the pressure force (which is proportional thereto). The heat released during the friction can cause heat to build up in the bearing temperature is too high and fast to use it, so you must strive to achieve as little friction.
Distinguish between friction:
- Dry, at which mating parts are not lubricated.
- Smooth as between the pin and bushing surfaces is always a layer of grease.
- Mixed mating surfaces where some contact (mainly on the tops of inequality), while in other areas are separated by a layer of grease.
The journal bearings seeks to achieve fluid friction, but in practice there is usually mixed friction. Working bearings in dry friction conditions (without lubrication) is not used. Obtaining a fluid friction is possible by providing conditions such that the lubricant is in a constant gap between the pin and the bush. This condition is met when the pressure grease in the gap is not greater than the pressure on the individual pin bush. It is also desirable that the working part of the pan was deprived of lubricating grooves.
Lubricants and Lubrication
The main task is to reduce friction lubricant between the mating surfaces, thereby reducing their consumption. Lubricants often the coolant.
Basic characteristics of lubricants are determined by:
- Dynamic viscosity, characterized by resistance to grease, that occurs when moving parallel surfaces: a unit of dynamic viscosity in the SI system is Pa * s;
- The kinetic viscosity, ie, the ratio of viscosity to density of the fluid (oil), as measured in m² / s;
- Lubricity, or the ability to permanently adhere to solid surfaces;
- Temperature and freezing point;
- Temperature Drop (for grease) at which the grease begins to melt;
- Resistance to aging, determines the frequency of relubrication.
Lubricants are distinguished: fixed, plastic and liquid, and on the grounds of:
Animal Vegetable Mineral
For the solid lubricants include solid materials, such as graphite, molybdenum disulfide, talc. They are used (usually in the form of a powder) rather rare, especially for use at high temperatures.
Grease (commonly referred to as constants) are formed by mineral oils, soaps density calcium, sodium, potassium, etc. are used in the bearings difficult to reach and seldom controlled.
For bearings are commonly used in liquid lubricants, and especially mineral oils. Because of the viscosity they are divided into spindle oil, machine, cylindrical.
Because of the way the lubrication lubrication passage stands out, circulation and immersion.
To apply grease reservoirs from which lubricant flows on the surface of the pin dropping temperatures beyond.
For pass-through lubrication (liquid lubricant) is used, among others wick lubricators or needle with adjustable flow.
Instruments used for lubrication
Circulation lubrication can be achieved by using rings loose or solid lubricants (both rings are partially submerged in the lubricant) or circulating pressure.
Material bearing on the bushings. Working bearing depends to a large extent on the properties of pairs of materials: the pivot bearings and bushings. Since the pins are usually steel shafts - a rather similar properties - so in order to obtain the best possible working conditions should be selected bearing materials bearing bushings (bearing materials).
In the selection of bearing materials must therefore be guided by the characteristics of those that are most relevant to the job specific bearings.
Since the bearing material therefore requires a high mechanical resistance to static and dynamic loads, seizure resistance, corrosion resistance, low coefficient of friction, a suitable thermal expansion, good thermal conductivity, good formability, good workability and low price. Although there is a lot of bearing materials, none of them satisfies all the requirements.
For the commonly used materials include bronze casting of lead and tin of high hardness and strength, brasses have a lower strength, but improved resistance to work at elevated temperature.
For special purposes apply multi layered shells, such as pan-coated steel with a thickness of the silver layer 0,50,75 mm and then a layer of lead (about 0.05 mm) with IDU.
If lubrication is difficult or because of working conditions should be avoided (in the traditional form) should be used with porous shells. Most are bush pressed, sintered and saturated with oil.
In addition to metal alloys used for the bearing shells, other materials, such as hardwood (gwajak or oak), plastics (mainly phenolic resins, polyamides, Teflon, etc.), rubber and graphite. The precise mechanisms of the bearings are used precious stones (ruby, sapphire), glass and other materials.
Construction bearings - radial bearings
The main part of the body is a slide bearing in which the pivot is mounted directly or indirectly.
Intermediate element is usually mounted in the housing sleeve, the inner surface of the bearing bushing. Bush may be poured bearing alloy layer. bearing bushes bearing parts are interchangeable, and may be single or bipartite.
For large deflection shafts are various types of pan-aligning (caster).
Bearing bushes should be secured against rotation and against axial displacement, the protection element (such as a pin) should not hinder the installation and removal.
Transverse body bearings are formed as separate pieces of machinery.
Accuracy of bearings - bearing clearances.
In determining the value of play, including take into account the roughness of the surface, differential thermal expansion of the material of the bearing material and the spigot, the maximum heating temperature of the bearings, the need to obtain a stable operation of the shaft at different temperatures.
Thrust bearings
The main thrust bearings are used to withstand loads when the working shaft in the vertical position. The bearings are lubricated under pressure. In larger bearings used such acetabular segment. Bearing surfaces of the segments are shaped so as to allow the production of a lubricating wedge, and to obtain fluid friction.
Bearings
Construction and division:
Working roller bearing characterized in that the effect of the rolling elements rolling between the surfaces of the ring of the rings and balls is called rolling friction.
There are also other varieties of roller bearings and needle roller bearings without cage or without inner ring and the cylindrical roller bearings without outer ring
The outer ring of the bearing is seated body in the slot machine or bearing housing and the inner ring - the pivot shaft. Cage is used to provide a uniform placement of the rolling elements on the circumference of the bearing.
The bearings of the present contact stress due to the almost point or linear contact with the raceways of the rolling elements, and therefore it is made of steel with special properties, especially hardness and high wear resistance.
Bearings are divided into: transverse, longitudinal and oblique, able to carry loads perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the shaft or running along its axis of rotation, and capable of handling both types of loads.
Depending on the shape of the rolling elements are distinguished and roller bearings. Rolls may be the shape of a cylindrical, conical or spherical.
Types of bearings
Division of rolling bearings by the main design features and bearing markings
Embedding bearings on shafts and housings machines
Embedding bearings should ensure establishment of the shaft and thrust bearings and obtain proper bearing clearance in the bearing during operation.
Longitudinal proper determination is that the one bearing shaft fixed in the longitudinal direction, ie, a fixed position and the pivot shaft resp. machine, and the other bearing should be able to traverse the longitudinal rel. the body, in order not to hinder thermal deformation of the shaft and to prevent excessive stresses due to defects such as assembly.
The most frequently used method of determining the longitudinal:
However, it also applies the bearings on the shaft mounting with lock nuts and washers gear. Rings, thrust bearings are also setting with circlips.
Failure to observe the principle of longitudinal setting can lead to deadlock the rolling elements and bearing damage.
Jobs bearings
Considering the conditions of the bearing, there are two basic load cases bearings:
- When moving a shaft (the most common case in practice)
- When moving a binding
In the first case, the inner ring is mounted tightly and the outer with a small bulk, and the second is inversely
Accuracy of bearings.
In determining the value of play, including take into account the roughness of the surface, differential thermal expansion of the bearing material, the maximum heating temperature of the bearing, the need to obtain a stable operation of the shaft at different temperatures.
Inserting and removing bearings
Smaller bearings are usually injected with a hammer and sleeve or with the press, noting the alignment of the bearing bore and shaft end. In order to facilitate the fitting of the bearing in an oil heated to a temperature 80 - 90 ° C. When inserting or removing the bearing should be observed that the force used for installing or removing did not work on the rolling elements.
Bearings are removed in order to:
- Replacement of bearings used
- Permit replacement of other components mounted on the shaft
Mechanical means of removing bearings:
Lubrication and sealing
The rolling bearing grease meets the following tasks:
- Reduces the consumption of surface raceways and rolling elements
- Transfers heat
- Protects the bearings from dirt and moisture
Depending on the type of lubricant and the lubrication system must be adequately sealed bearings, protecting them against lubricant leakage.
Bearing the seal of distinction, among others, Shielded bearings, bearings with rubber gaskets and bearings sealed on both sides (face down) - which are filled with grease, which lasts for the life of the bearings.